The Importance of Fog in Microclimates
Understanding Fog and Microclimates Fog plays a significant role in shaping microclimates, which are localized atmospheric zones with climatic conditions differing from their surrounding areas. Understanding the interaction between fog and microclimates can provide insights into environmental variability and its impact on […]
Understanding Fog and Microclimates
Fog plays a significant role in shaping microclimates, which are localized atmospheric zones with climatic conditions differing from their surrounding areas. Understanding the interaction between fog and microclimates can provide insights into environmental variability and its impact on ecosystems and human activities.
Formation of Fog
Fog is essentially a collection of water droplets suspended in the air near the earth’s surface. It forms when the air near the ground cools to its dew point, allowing moisture to condense into visible water droplets. This phenomenon is most common in areas with high humidity and rapid cooling conditions, such as coastal regions.
Fog formation involves the interaction of several atmospheric elements. Temperature, humidity, and wind patterns all contribute to its development. As the air cools, often due to loss of heat from the ground at night, it reaches the dew point where moisture in the air condenses to form fog. The specific conditions under which fog forms can vary, creating different types of fog.
Types of Fog
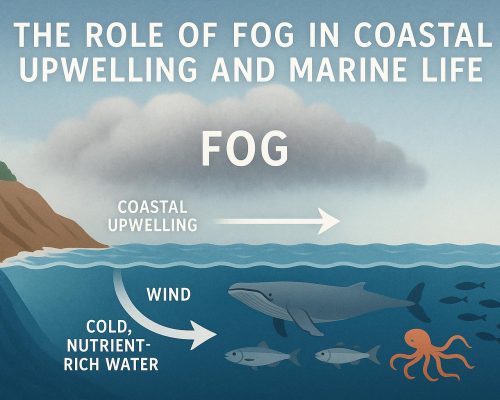
Several types of fog exist, such as radiation fog, which forms on clear nights as the earth’s surface loses heat, and advection fog, which occurs when warm, moist air passes over a cooler surface. Sea fog or coastal fog typically arises when warmer ocean air moves over the cooler land and is prevalent in areas such as California’s coast.
Radiation fog is perhaps the most common type, occurring when the earth emits thermal energy and cools the ground significantly under calm conditions, leading to condensation as the temperature reaches the dew point. Advection fog, on the other hand, requires the horizontal movement of moist air over a cooler surface, such as ocean air moving over land masses. Sea fog is a variant of advection fog but specific to maritime climates where this phenomenon can create persistent clouds of moisture hovering over coastal landscapes.
Fog Dissipation
The dissipation of fog is as critical as its formation. As the sun rises and heats the ground, the surface temperature increases, reducing relative humidity and causing fog to evaporate. Wind can also contribute to dispersing fog by mixing air layers and promoting evaporation. However, dense fog can persist, especially in valleys and low-lying areas where air circulation is limited.
The Role of Fog in Microclimates
Fog contributes to the development of distinct microclimates due to its ability to affect local temperature, humidity, and sunlight exposure. Areas frequently shrouded in fog often experience cooler temperatures and higher humidity compared to nearby clear regions.
These microclimatic conditions are crucial to both terrestrial and marine ecosystems. In regions like California’s coast, fog frequently blankets the landscape, creating a cooler and more humid environment than areas further inland, which can significantly influence local flora and fauna.
Impacts on Vegetation
Fog can significantly influence plant life by providing essential moisture and reducing water stress during dry periods. Coastal redwoods in California, for instance, rely heavily on fog drip to meet their water needs. This dependency illustrates how fog can support biodiversity and enable unique ecosystems to thrive.
Fog acts as a critical moisture source for many plants, particularly in arid and semi-arid regions. Through a process known as ‘fog drip,’ where fog condenses on leaves and other surfaces, plants can acquire water even when rainfall is scarce. This process enables species like the coastal redwoods to sustain themselves in regions where soil moisture from precipitation is insufficient.
Impacts on Agriculture
In agricultural settings, understanding fog’s influence on microclimates can improve crop management and yield. Farmers may leverage fog’s cooling effects and additional moisture in regions where water resources are scarce. However, excessive fog may also hinder plant growth by limiting sunlight exposure, necessitating balanced approaches to agricultural planning.
The cooling effect of fog can be beneficial in preventing heat stress on crops, while the moisture it brings can supplement irrigation. However, the downside to persistent fog is a reduction in sunlight, which can slow down photosynthesis and plant development. Therefore, farmers in fog-prone areas often need to adapt their planting schedules and select crop varieties that can tolerate such conditions.
Fog and Human Activities
Fog’s impact extends to various human activities, especially in transport and urban planning. Reduced visibility due to fog can pose significant challenges for aviation and road transport, necessitating advanced navigation and safety measures. Furthermore, urban areas prone to fog may require specific architectural and infrastructural adaptations to mitigate its effects.
Navigation systems, especially in aviation, often incorporate advanced radar and GPS technology to manage the risks posed by fog. In urban design, considerations might include the placement of buildings and roads to accommodate reduced visibility and the unique microclimates created by frequent fog.
Technological Adaptations
To address the challenges posed by fog, technologies such as fog nets or water catchment systems have been developed to harness fog’s moisture for agricultural and drinking purposes in arid regions. This innovation underscores fog’s potential to contribute positively to human livelihoods when managed effectively.
Fog nets, which capture moisture from fog and channel it into storage containers, have proven invaluable in regions with limited freshwater sources. These systems are particularly prevalent in areas along the west coasts of South America and Africa, where they supplement water supplies for agriculture and community use.
Fog Monitoring and Forecasting
Accurate fog monitoring and forecasting are crucial for mitigating the impacts of fog on transportation and urban activities. Weather stations equipped with devices to measure temperature, humidity, and dew point are essential for predicting fog formation. Advances in remote sensing and satellite technology continue to enhance these capabilities, providing more precise data on fog occurrence and expected dissipation.
Conclusion
Understanding the importance of fog in shaping microclimates provides valuable insights into ecological and human systems. By appreciating fog’s role in environmental and climatic processes, stakeholders can better manage natural resources and adapt to changing conditions worldwide. For further reading on climate science, you might explore resources from NASA or NOAA.